Health - ADDICTION TYPES - ALCOHOL: How does alcohol cause CANCER?

The less alcohol you drink, the lower the risk of cancer. No type of alcohol is better or worse than another, it is the alcohol itself that leads to the damage, regardless of whether it is in wine, beer or spirits. And drinking and smoking together are even worse for you.
Not everyone who drinks alcohol will develop cancer. But on the whole, scientists have found that some cancers are more common in people who drink more alcohol than others. Every year, alcohol causes 4% of cancers in the UK, around 12,800 cases.
Read more about the evidence that alcohol causes cancer.
Which is worse: binge drinking or spreading my drinking across the week?
Research has looked mainly at the amount of alcohol people drink in total and the effect on cancer risk. Drinking alcohol increases the risk of cancer whether you drink it all in one go or a bit at a time.
How much alcohol does it take to increase cancer risk?
There’s no ‘safe’ limit for alcohol when it comes to cancer, but the risk is smaller for people who drink within the government guidelines.
Read more about how to cut down on alcohol.
Regularly drinking up to a pint of premium lager or a large glass of wine a day can increase the risk of mouth, throat, oesophageal (foodpipe), breast and bowel cancers. They both include about 3 units of alcohol.
Each unit of alcohol has a weaker effect on the risk of breast cancer than on cancers of the head and neck, but because breast cancer is the most common cancer in the UK and because so many women drink small amounts of alcohol regularly, a large number of women are affected - around 3,200 cases of breast cancer each year in the UK are linked to alcohol.
Which cancers are affected?
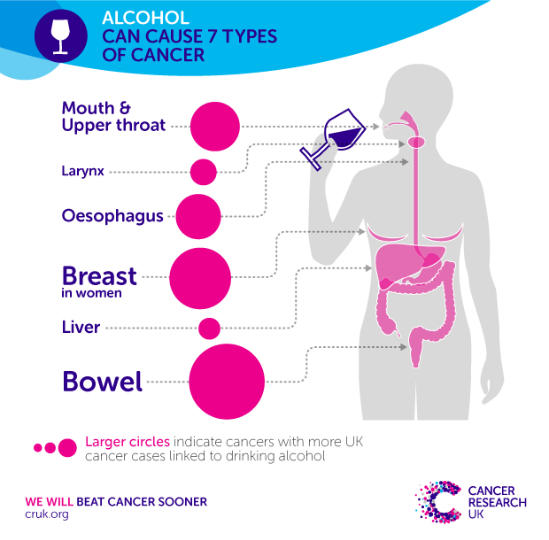
Drinking alcohol regularly can increase the risk of at least 7 different cancers. It is likely that different cancers are caused in different ways. Cancers linked to alcohol include:
- Mouth cancer
- Pharyngeal cancer (upper throat)
- Oesophageal cancer (food pipe)
- Laryngeal cancer (voice box)
- Breast cancer
- Bowel cancer
- Liver cancer
What is acetaldehyde and how can it cause cancer?
In our bodies, alcohol (ethanol) is converted into a toxic chemical called acetaldehyde.
It can cause cancer by damaging DNA and stopping our cells from repairing this damage. The International Agency for Research on Cancer has classified acetaldehyde formed as a result of drinking alcohol as being a cause of cancer, along with alcohol itself.
Acetaldehyde also causes liver cells to grow faster than normal. These regenerating cells are more likely to pick up changes in their genes that could lead to cancer.
Ethanol is broken down mainly by the liver, but lots of other cell types can do this as well. Some of the bacteria that live in our mouths and the linings of our guts are also able to convert ethanol into acetaldehyde.
How can alcohol’s effects on oestrogen and other hormones lead to cancer?
Alcohol can increase the levels of some hormones, such as oestrogen. Hormones act as messengers in the body, giving our cells instructions such as when to divide. Unusually high levels of oestrogen increase the risk of breast cancer.
Why is it worse to both drink and smoke?
People who smoke and drink multiply the risk for certain cancers, because tobacco and alcohol work together to damage the cells of the body. For example, alcohol makes it easier for the mouth and throat to absorb the cancer-causing chemicals in tobacco. This is one reason why people who drink and smoke multiply the damage they receive and have especially high risks of cancer.
Can liver damage lead to cancer?
Drinking lots of alcohol can damage the cells of the liver, causing a disease called cirrhosis. Cirrhosis can make you more likely to develop liver cancer.
What about folate?
Folate is an important vitamin that helps our cells produce new DNA correctly. People who drink alcohol tend to have lower levels of folate in their blood and some studies have found that some cancers are more common in people with low folate levels. But at the moment it isn’t clear if alcohol does cause cancer in this way, or whether the amount of folate people get in their diet affects the risk from alcohol.
How else can alcohol damage DNA?
Alcohol can cause highly reactive molecules, called Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), to be produced in our cells. These molecules can damage the DNA, which could cause cancer to develop.